F5 SSL Orchestrator

Do you know how to protect encrypted traffic? Have you wondered how encrypted traffic is protected today? How to defend against attacks that are hidden in encrypted traffic? 70% percent of today's internet traffic is encrypted, 80% of websites today are encrypted using SSL/TLS.
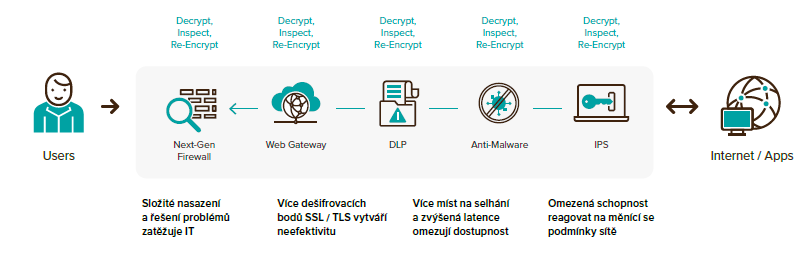
In the contemporary landscape, for businesses and their software to consistently function effectively with network traffic, it is imperative that their web applications or traffic be securely encrypted. This, on the one hand, brings the confidence of users on the other, increased demands on performance to ensure protection and encrypted traffic. This also entails room for malware, because these attacks now take place in encrypted traffic, and due to the amount of data that is encrypted, there is a high chance that the attacker will not be detected. Whether due to the amount of encrypted data or the insufficient performance of the devices responsible for protection. Therefore, performance is absolutely key in this part of security.
The encrypted traffic protection model below is nowadays mainly built on the model of decryption and subsequent encryption before proceeding to the next device. This entails a complex deployment of elements and a subsequent burden for IT in their management, inefficiency and wasted device performance , due to multiple decryption and subsequent re-encryption. The number of elements also carries the risk of more failure possibilities, and among the not-negligible consequences is also increased latency with regard to the availability of services.
Encrypted traffic with F5 SSL orchestrator
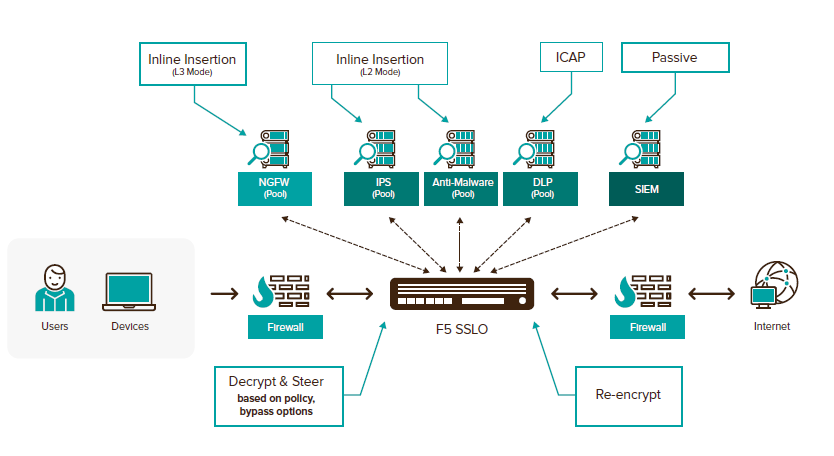
For the above reasons, the F5 company comes up with a solution in the form of an SSL Orchestrator , which decrypts all traffic (SSL/TLS), then directs it to the appropriate device for further control (NGFW, IPS, DLP, WSA) and then sends it back encrypted. This brings significant savings for devices whose performance will be sufficient for a longer period of time and they can use it for the purposes for which they are deployed in the network.